Flex License Model
The Flex License model is a network-wide license for WebRTC, SIPREC and SBC capacity, managed by AudioCodes OVOC, which is dynamically shared among multiple devices. The Flex License is ordered as a single license, which provides a pool of these licenses that cannot be exceeded. The Flex License pool includes the following capacity license types:
|
■
|
"SBC Sessions" - maximum number of concurrent SBC call sessions (media and signaling) |
|
■
|
"Far End Users" - maximum number of SIP endpoints (user agents) that can be registered with the device |
|
■
|
"WebRTC Sessions" - maximum number of WebRTC sessions |
|
■
|
"SIPREC Streams" - maximum number of SIPREC sessions |
|
■
|
"SIPREC Redundancy Streams" - maximum number of SIPREC sessions for the standby SRS in the active-standby redundancy pair |
The Flex License model supports WebRTC and SIPREC capacity licensing only from OVOC Version 8.0.3000 and later. If you are using an earlier OVOC version, WebRTC and SIPREC capacity is according to your local License Key only.
The Flex License model is similar to the Floating License model (as described in Floating License Model), but provides some important advantages:
|
■
|
The Flex License is solely managed by OVOC; it doesn't employ a cloud-based license manager like the Floating License. This reduces the exposure of OVOC to security risks from its connectivity with the public cloud. |
|
■
|
The Flex License gracefully enforces license capacity of the pool, whereas the Floating License allows devices to exceed pool capacity, resulting in you being billed at the end of the month for unexpected license usages. |
The Flex License is managed by OVOC, which defines the devices using the Flex License. Once connected to OVOC, each device can handle calls using the licenses of the different license types in the Flex License pool, as long as the pool has available (unused) licenses. However, the device's capacity is limited by its inherent maximum capacity support and by an optional user-defined limit called Allocation Profile (discussed later in this section), which specifies a capacity that is less than the device's inherent capacity per license type.
The devices periodically (typically, every five minutes) report their current license consumption (usage) per license type to OVOC. OVOC uses these reports to calculate the total number of currently used licenses from the pool and therefore, determines the remaining licenses in the pool per license type. To view the license usage reports, see Viewing Floating or Flex License Reports.
Each device in OVOC is configured with a priority level (Low, Normal, or Critical). When all the licenses of a specific license type in the Flex License pool are being used (or even exceeded) by the devices, OVOC uses this priority level to determine which of the devices to initially "take out" of service. OVOC first notifies a certain percentage of devices of this "over-license" status, instructing them to reject all new calls that require this specific license type. This percentage of devices starts from those with Low priority level, then Normal priority level, and lastly Critical priority level.
For example, assume there are 100 devices in the network, 10 configured with Low priority, 20 with Normal priority, and 70 with Critical priority, and OVOC notifies 20% of them of an "over-license" state for a specific license type. In this example, OVOC takes out of service the 10 devices with Low priority and 10 devices with Normal priority (i.e., total of 20, which is 20% of 100). This selective process allows devices with higher priority to continue providing call service, while attempting to restore licenses to the Flex License pool due to the rejection of new calls by the selected devices. During this period, the devices send their usage reports more frequently to OVOC, providing OVOC with a more up-to-date status of license usages in the network. If licenses become available for the specific license type in the pool, OVOC allows the selected devices to start accepting new calls ("ok" status). However, if after a certain period there are still unavailable licenses for the specific license type in the pool, OVOC notifies all devices (including those with Critical priority level) of this "over-license" status, and instructs all of them to reject new calls. To view the device's current license utilization (in percentage) per license type of the OVOC Flex License pool and the status ("ok" and "overlicense") of each license type, see Viewing Flex License Utilization and Status.
Connection between the devices and OVOC is established over SNMP and functionality of the Flex License service is managed over TCP/HTTPS REST. If the device loses connectivity with OVOC, the device continues handling calls for a graceful period. If connectivity is not restored when this period expires, the device is blocked from handling new calls. When the device succeeds in connecting again with OVOC, it continues using the Flex License pool as normal.
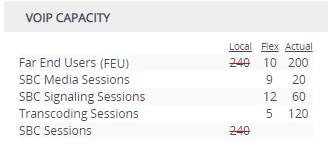
When the device uses the Flex License, the License Key page (see Viewing the License Key) displays "Flex License" in the 'Mode' field and displays the licensed capacity received from the Flex License pool per license type under the VoIP Capacity group, as shown in the following example:
|
■
|
'Local': Displays the number of licensed capacity per license type from the locally installed License Key. These licenses are not used by the device and the figures are displayed crossed out (strikethrough). |
|
■
|
'Flex': Displays the maximum number of licensed capacity per license type in the OVOC Flex License pool. |
|
■
|
'Actual': (This column can be ignored.) |
After a device restart, the figures in the 'Flex' column appear only after the device receives its first report from OVOC on the Flex License pool capacity. This typically takes about five minutes.
The device sends the following SNMP alarms to indicate various conditions relating to the OVOC Flex License pool:
|
■
|
acFloatingLicenseAlarm: Sent if you have configured an Allocation Profile that exceeds the device's resource capability. |
|
■
|
acCloudLicenseManagerAlarm: Sent upon various conditions such as loss of connectivity between device and OVOC. |
For more information, refer to the document SBC-Gateway Series SNMP Alarm Reference Guide.
|
●
|
For configuring the Flex License on OVOC, refer to the document OVOC User's Manual, which can be downloaded from AudioCodes website. |
|
●
|
The Fixed License only provides WebRTC, SIPREC and SBC capacity licenses (listed in the beginning of this section). Therefore, your device must still be installed with a local License Key to enable other ordered license-based features (e.g., Test Call) and capacity. |
|
●
|
The Flex License cannot operate with the other OVOC-managed license modes (e.g., Fixed License and Floating License). Therefore, before enabling the Flex License, make sure that the other license modes are disabled on OVOC. |
|
●
|
The Flex License ignores OVR, and LAD capacity licenses in the local License Key. |
